What should individuals do to migrate climate change ?
climate change.
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns. These shifts may be natural, but since the 1800s, human activities have been the main driver of climate change, primarily due to the burning of fossil fuels (like coal, oil, and gas), which produces heat-trapping gases.
How climate is changing?
The footprint of climate change can already be seen in every corner of the planet. Erratic weather patterns, rising sea levels and melting glaciers due to climate change, are reshaping societies across the globe. Through multilingual news and expert analysis, the third pole captures how these changes are unfolding in India, one of the world’s most climate vulnerable countries. In India, climate change is already affecting human health, wildlife, food production, clean water access and the economy at large.
But in the case of India, these vulnerabilities come with a unique potential for change. Home to nearly 20% of the world’s population, the country is looking to transform its fast growing infrastructure and energy systems to reduce heat trapping emissions on a massive scale.
The outcome of these efforts are globally important, as India is the third largest greenhouse gas emitter after China and the united states. Since those two nations have presented bold plans to achieve net zero emissions by 2060 and 2050 respectively, India is today facing increasing pressure to step up its ambitions too, becoming the next battleground of the global clean energy transition.
![Temperature anomaly (°F)
2
GL |.
1] oli
lpr
-1
Lower troposphere
2 Earth's surface (measured by satellite)
am === UAH RSS
3
1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020
Year](https://contents.bebee.com/users/id/9dexr6398ad6cba44e/article/what-should-individuals-do-to-YJrWyv3tpgON/j5FJs.png)
- Gases responsible for climate change.
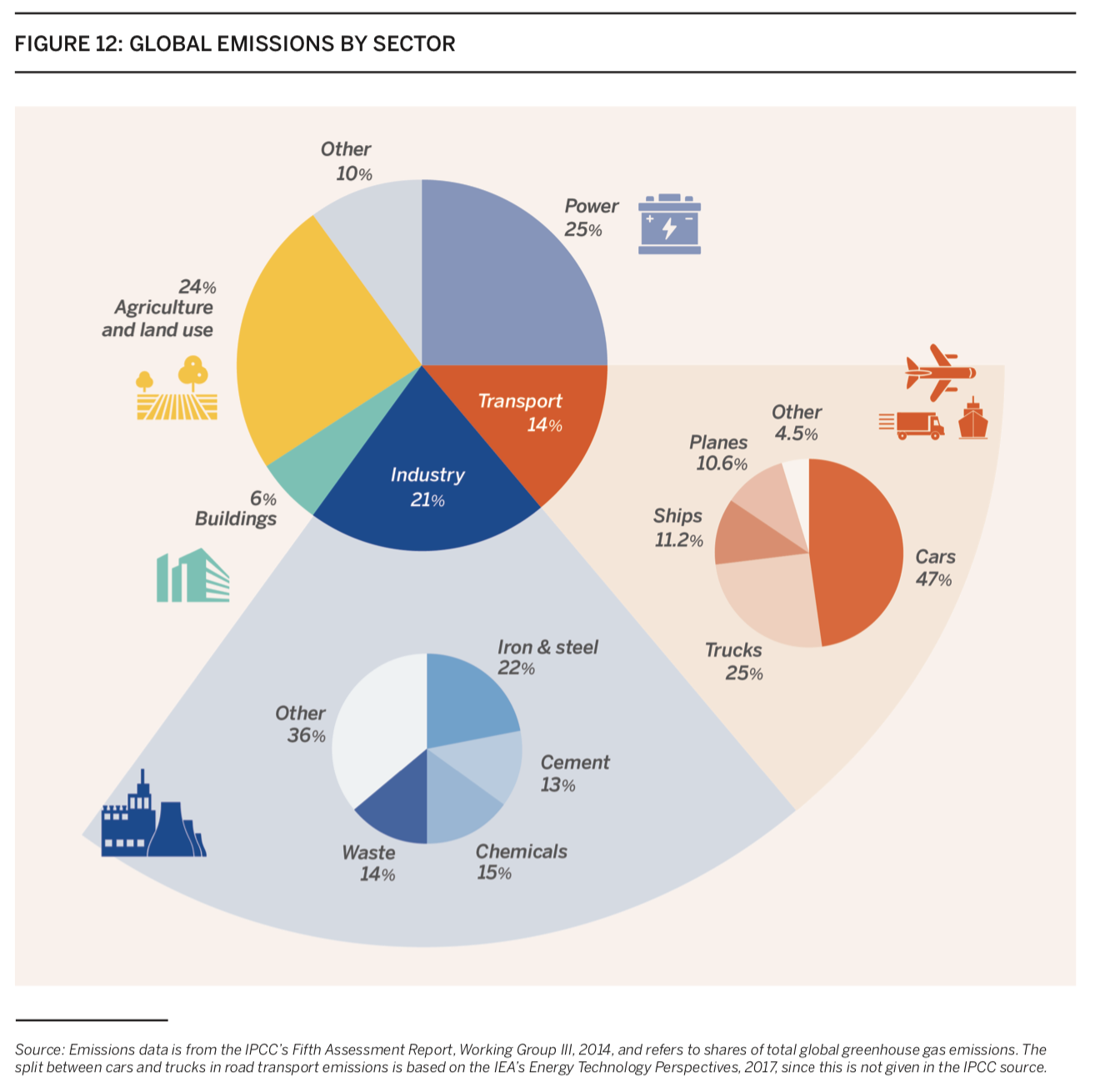
The largest anthropogenic (human caused) source of carbon dioxide emissions is the global energy system, which means transforming the global energy system is one of the most significant ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change.
As of 2019, approximately 81% of the world’s primary energy supply still comes from fossil fuels, (specifically, coal, oil, and natural gas), which result in carbon emissions both upstream (in the extraction and production of the energy) and downstream (during the final consumer use of the energy). continued reliance on fossil fuel-based energy sources is a barrier to emissions reductions, particularly as energy demand continues to increase around the world.
Global warming of 1°c or 1.5°c represents an average across the planet – many places will warm faster, and see far greater temperature increases. For example, the arctic is warming 2-3 times faster than any other place on earth. The effects of global heating are far-reaching, including rising sea levels, glacier retreat, changes in the timing of seasonal events (plants flowering, migration patterns), and a rise in the frequency and severity of extreme weather events. These categories of impacts have direct and indirect consequences on people and wildlife. Direct consequences include displacement of people and communities due to sea level rise and extreme weather events, whereas indirect consequences may include disruptions to economic development, food production, escalation in water crises, and increased public health risks.
The impacts of climate change will not be evenly felt around the world – people living in the poorest countries and in geographically vulnerable regions (such as small-island states) will be first and most significantly impacted. This is because communities living in poverty are more likely to be exposed to environmental hazards, are often more dependent on natural resource-based livelihoods such as agriculture, and have fewer resources to cope with climate impacts.
- MAIN SOURCE WHICH ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR THE CLIMATE CHANGE.
Fossil fuels – coal, oil and gas – are by far the largest contributor to global climate change, accounting for over 75 per cent of global greenhouse gas emissions and nearly 90 per cent of all carbon dioxide emissions. As greenhouse gas emissions blanket the Earth, they trap the sun's heat.
1)Vehicles.
2) Factory.
Our personal vehicles are a major cause of global warming. Collectively, cars and trucks account for nearly one-fifth of all US emissions, emitting around 24 pounds of carbon dioxide and other global-warming gases for every gallon of gas. About five pounds comes from the extraction, production, and delivery of the fuel, while the great bulk of heat-trapping emissions—more than 19 pounds per gallon—comes right out of a car’s tailpipe.
In total, the US transportation sector—which includes cars, trucks, planes, trains, ships, and freight—produces nearly thirty percent of all US global warming emissions, more than almost any other.


1)Factory pollution. 2)Vehicle pollution.
- ALTERNATIVE FOR CRUDE OIL,PETROL AND DIESEL .
1) Biodiesel from Jatropha curcas. 2) Hydrogen fuel.
1) Biodiesel from Jatropha curcas.
Jatropha is a genus of flowering plants in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae. The name is derived from the Greek words ἰατρός, meaning "physician", and τροφή, meaning "nutrition", hence the common name physic nut. Another common name is nettlespurge.
- First, Jatropha oil is filtered to remove the solid particles present in it. Then it is heated to remove the water contents if present in it.
- Biodiesel is now used as a diesel engine in the number of agencies. The results are said to be comparable with petroleum in all areas like power, efficiency, climbing, hauling, etc.
- To determine the amount of catalyst that is required.
- The right amount of potassium hydroxide is mixed with methanol until the methanol completely dissolves to get potassium methoxide.
- In the winter season, additional Jatropha oil is heated and is mixed with the potassium methoxide.
- The mixture is allowed to settle. In this process, glycerin settles at the bottom and the biodiesel at the top. The glycerin is then removed, and the biodiesel is washed and dried.
- The biodiesel obtained is then checked for quality.
-


2)Hydrogen fuel.
Hydrogen fuel refers to hydrogen which is burned as fuel with oxygen. It is zero-carbon, provided that it is created in a process that does not involve carbon. It can be used in fuel cells or internal combustion engines.
- ELECTROLYTIC PROCESSES:- Water can be separated into oxygen and hydrogen through a process called electrolysis. Electrolytic processes take place in an electrolyzer, which functions much like a fuel cell in reverse—instead of using the energy of a hydrogen molecule, like a fuel cell does, an electrolyzer creates hydrogen from water molecules
2)SOLAR-DRIVEN PROCESSES.
- There are a few solar-driven processes, including photobiological, photoelectrochemical, and solar thermochemical.
- Photobiological processes use the natural photosynthetic activity of bacteria and green algae to produce hydrogen.
- Photoelectrochemical processes use specialized semiconductors to separate water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Solar thermochemical hydrogen production uses concentrated solar power to drive water splitting reactions often along with other species such as metal oxides.
3)BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES:- Biological processes use microbes such as bacteria and microalgae and can produce hydrogen through biological reactions. In microbial biomass conversion, the microbes break down organic matter like biomass or wastewater to produce hydrogen, while in photobiological processes the microbes use sunlight as the energy source.
- Advantages of Bio-fuels.
- Biodiesel is a domestically produced.
- clean-burning.
- renewable substitute for petroleum diesel.
- Using biodiesel as a vehicle fuel.
- increases energy security.
- improves air quality and the environment.
- provides safety benefits.
Science and Technology
You may be interested in these jobs
-

Business Development Associate Fresher Job
Found in: beBee S2 IN - 2 days ago
Urban Company (Formerly UrbanClap) Bangalore, India Full time· About the job: · Key responsibilities: · 1. Managing day-to-day operations · 2. Taking qualitative and quantitative measures to ensure demand-supply equilibrium · 3. Engaging in developing the overall category, handling business metrics, and creating immense opportunities for ...
-
AFM Assistant Floor Manager FM Floor Manager
Found in: Whatjobs IN C2 - 6 days ago
YO HR CONSULTANCY Jabalpur, IndiaAFM (Assistant Floor Manager) / FM (FloorManager) · Experience:58Years · Qualification:Graduates from anyStream · Responsibilities: · *Broking industryexperience · *Develop and maintain a longterm relationship with customers tomaintain a high level of retention of existing custom ...
-
Oracle OIC Tech
Found in: Talent IN C2 - 2 days ago
Chaitanya Placement Agency Chennai, IndiaCompanyOverview: · ChaitanyaPlacement Agency is a renowned IT staffing company providingmanpower assistance to its clients across the country. Operating inthe Staffing and Recruiting industry we specialize in connectingqualified professionals with toporganizations. · RoleandRespo ...


Comments