Management to the kidney stones
Abstract:
The Urolithiasis affects the 5-15% of the population worldwide. The Recurrence rates are close to upro 50% nd the cost of urolithiasis to individuals and society is high. As we can say that the Acute renal colic it is a common presentationn in general practice, so it is a basic understandingg of its evaluationn nd the treatment would be usefull. And the most of the literature is retrospective, but we will try to provide an evidence based review of the managemennt of the urolithiasis and will be the prospective randommised controlled trials when it is available.
Introduction:
Types of Stone Diseases and Risk Factor
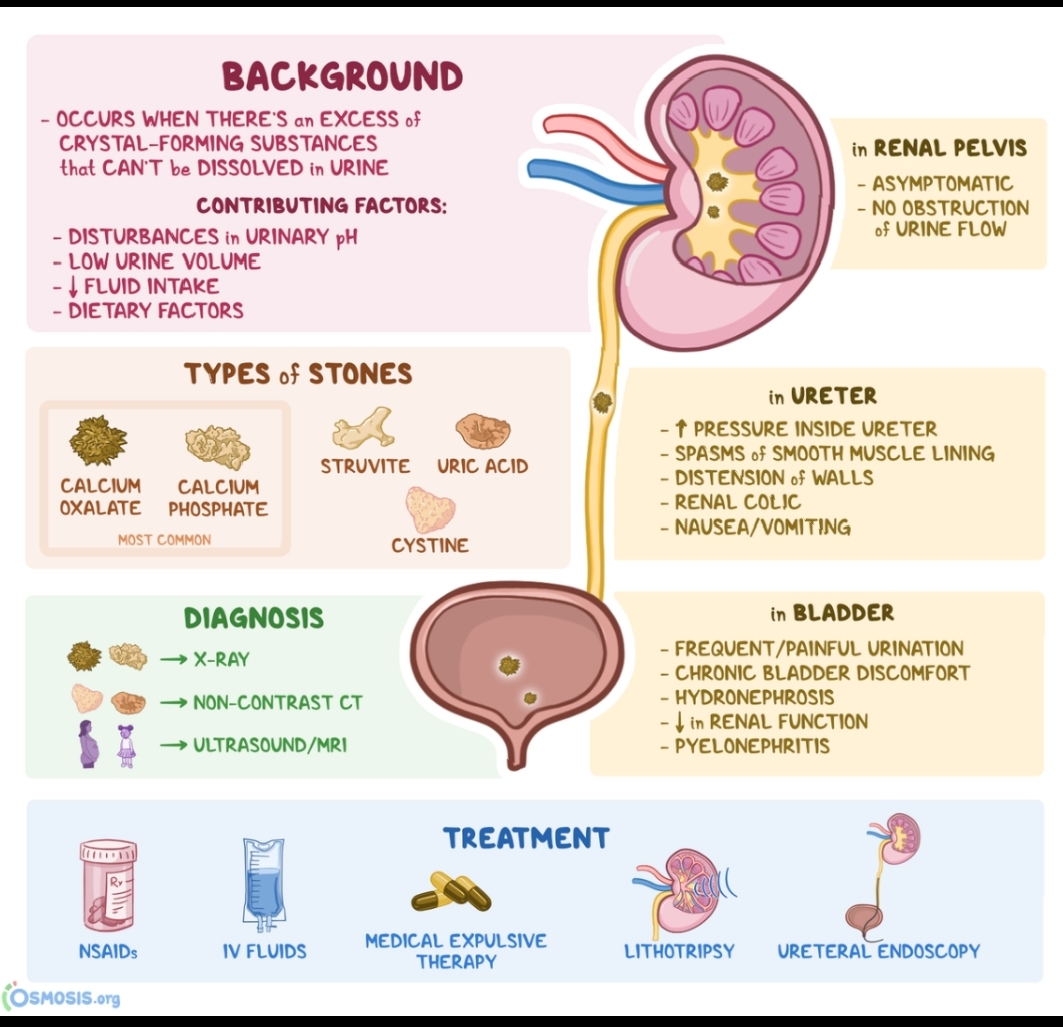
The kidney stones are made of the organic and the inorganic crystalss with proteins. Calcium stones are the most imp type, accounting for up to 80% (table1.)Of these, calcium oxalatee, calcium phosphate, struvite, and the cystine are the radio opaque stones, while the uric acid, Xanthine, and the hypoxanthine stones are the radiolucent. The risk factors for the stone disease are as shown in the (Table 2.)
Table 1. Types of stones
Table 2. Risk factors for stone disease
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
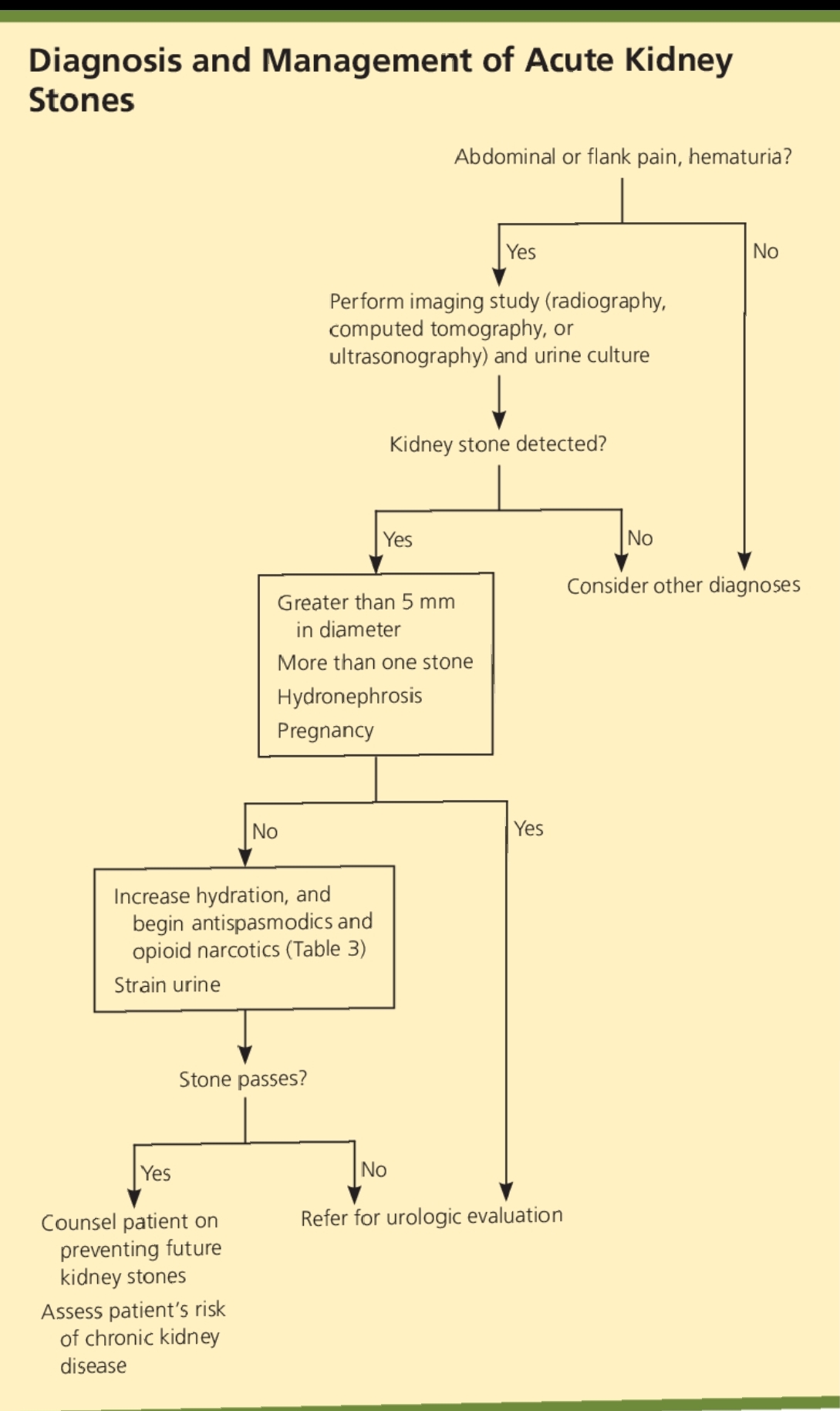
if we talked about the Acute renal colic presents as the cramping and the intermittennt abdominal and the flank pain as the kidney stones travel down the uretter from the kidney to the bladder. The Pain is often by the nausea, vomiiting, and the malaises, and fever and chills are may also be present. The Similarity with a previous episode be should increased with confidence in the diagnosis, And the value of personal or family historry during an episode of renal colic is not known.....
The physical examination should be directed toward excluding the differentials diagnoses (e.g., Like as the urinary tract infection, nd the musculoskelettal inflammation or spasms, the ectopic pregnancy, testiicular torsion, and the malignancy. The initial workup of the a patient with suspectedd with the kidney stones in the primary care setting should include poor point of care urinalysis is to detect the blood, because hematuria helps and to confirm the diagnosis.
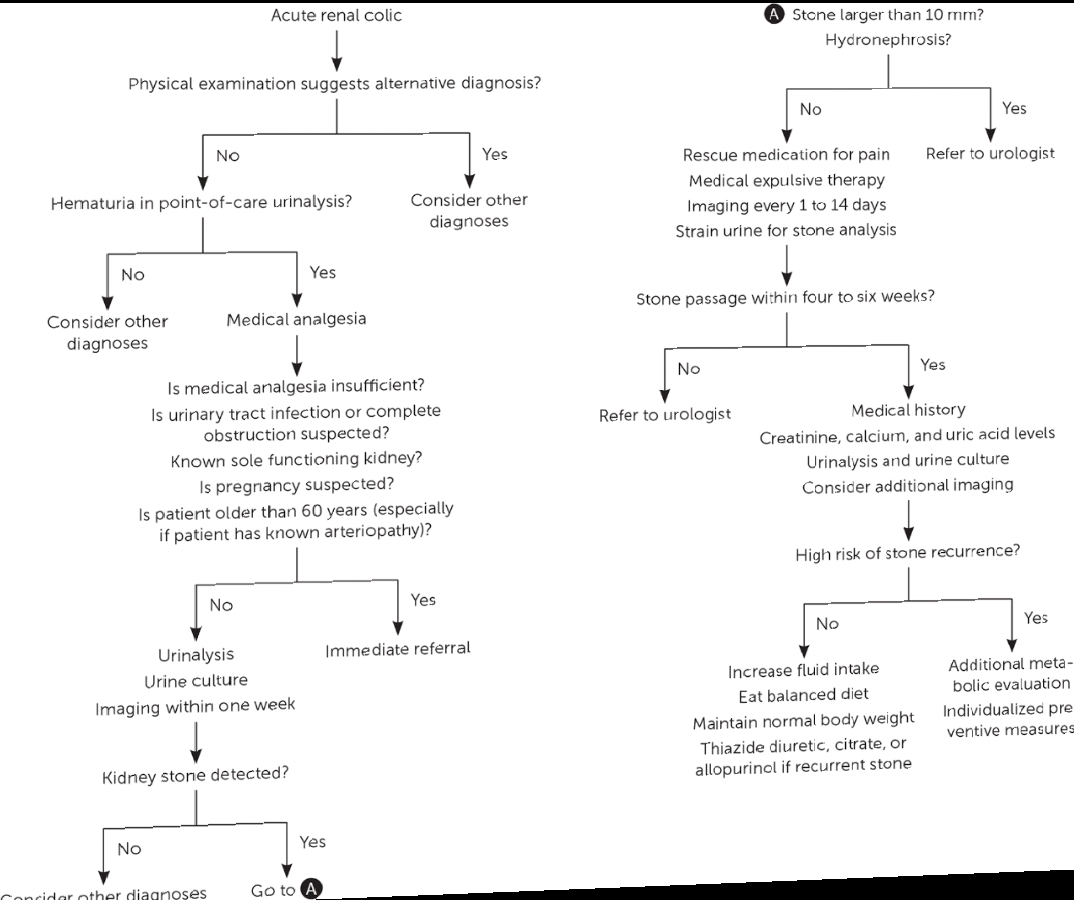
Algorithm for the diagnosis and management of acute kidney stones
Management to the stones:
Most of the kidney stones are small enough to be passed out in your pee and can probablly be treated at the home.
Treating small kidney stones
The Small kidney stones may cause pain until you pass them, which usually takes one or the two days.
A general practitioner may be recommend to a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAIDs), to help with the pain.
To ease your symptoms, a General practitioner might also be recommend:
The drinking plenty of fluids throughout the day and the
anti-sickness medicine
Like as the alpha-blockers (medicines is to to helps the stones pass)
And You might be advised to drink up to 3 litres (5.2 pints) of fluid throughout the day, every day, until the stones have cleared.
To help your stones pass:
drink water, but drinks like tea and coffee also count
add fresh lemon juice to your water
avoid fizzy drinks
do not eat too much salt
Make sure you're drinking enough fluid. If your pee is dark, it means you're not drinking enough. Your pee should be pale in colour.
You may be advised to continue drinking this much fluid to prevent new stones forming.
If your kidney stones are causing severe pain, your GP may send you to hospital for tests and treatment.
Treating large kidney stones
If your kidney stones are too big to be passed naturally, they're usually removed by surgery.
Surgery for treating kidney stones
The main types of surgery for removing kidney stones are:
shockwave lithotripsy (SWL)
ureteroscopy
percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
Your type of surgery will depend on the size and location of your stones.
Shock wave lithotripsy (SWL)
SWL involves using ultrasound (high-frequency sound waves) to pinpoint where a kidney stone is.
Ultrasound shock waves are th
PC en sent to the stone from a machine to break it into smaller pieces so it can be passed in your urine.
SWL can be an uncomfortable form of treatment, so it's usually carried out after giving painkilling medication.
You may need more than 1 session of SWL to successfully treat your kidney stones.
Ureteroscopy
Ureteroscopy involves passing a long, thin telescope called a ureteroscope through the tube urine passes through on its way out of the body (the urethra) and into your bladder.
It's then passed up into your ureter, which connects your bladder to your kidney.
The surgeon may either try to gently remove the stone using another instrument, or they may use laser energy to break it up into small pieces so it can be passed naturally in your urine.
Ureteroscopy is carried out under general anaesthetic, where you're asleep.
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) NL involves using a thin telescopic instrument called a nephroscope.
A small cut (incision) is made in your back and the nephroscope is passed through it and into your kidney.
The stone is either pulled out or broken into smaller pieces using a laser or pneumatic energy.
PCNL is always carried out under general anaesthetic.
Complications of treatment
Complications can occur after the treatment of large kidney stones.
Your surgeon should explain these to you before you have the procedure.
Possible complications will depend on the type of treatment you have and the size and position of your stones.
Complications could include:
sepsis, an infection that spreads through the blood, causing symptoms throughout the whole body
a blocked ureter caused by stone fragments (the ureter is the tube that attaches the kidney to the bladder)
an injury to the ureter
a urinary tract infection (UTI)
bleeding during surgery
pain
Prevention
The best way to prevent kidney stones is to make sure you drink plenty of water each day to avoid becoming dehydrated.
To prevent stones returning, you should aim to drink up to 3 litres (5.2 pints) of fluid throughout the day, every day.
You're advised to:
drink water, but drinks like tea and coffee also count
add fresh lemon juice to your water
avoid fizzy drinks
do not eat too much salt
Keeping your urine clear helps to stop waste products getting too concentrated and forming stones.
Conclusions:
Kidney stones present as an important and challenging clinical problem. Medical therapy, when used judiciously in conjunction with dietary measures, can help in preventing recurrence and in expulsion of small size (<10 mm) stones. Awareness of the advantages and limitations of different modalities of medical therapy is necessary in order to provide the correct treatment to pateints presenting with this common complaint.
References:
Nicole L Miller, fellow in endourology and minimally invasive surgery and James E Lingeman, physician and surgeon
Kidney Stones: Treatment and Prevention.
LEONARDO FERREIRA FONTENELLE, MD, MPH, PhD, AND THIAGO DIAS SARTI, MD, MPH, PhD
Medical management of renal stone
Shriganesh R. Barnela, Sachin S. Soni,1,2 Sonali S. Saboo,1 and Ashish S. Bhansali3
Articles from Aasif Aasif
View blog
Abstract: · All Around the world, snake bite is the · envenomation it is Envenomation it is the nam ...
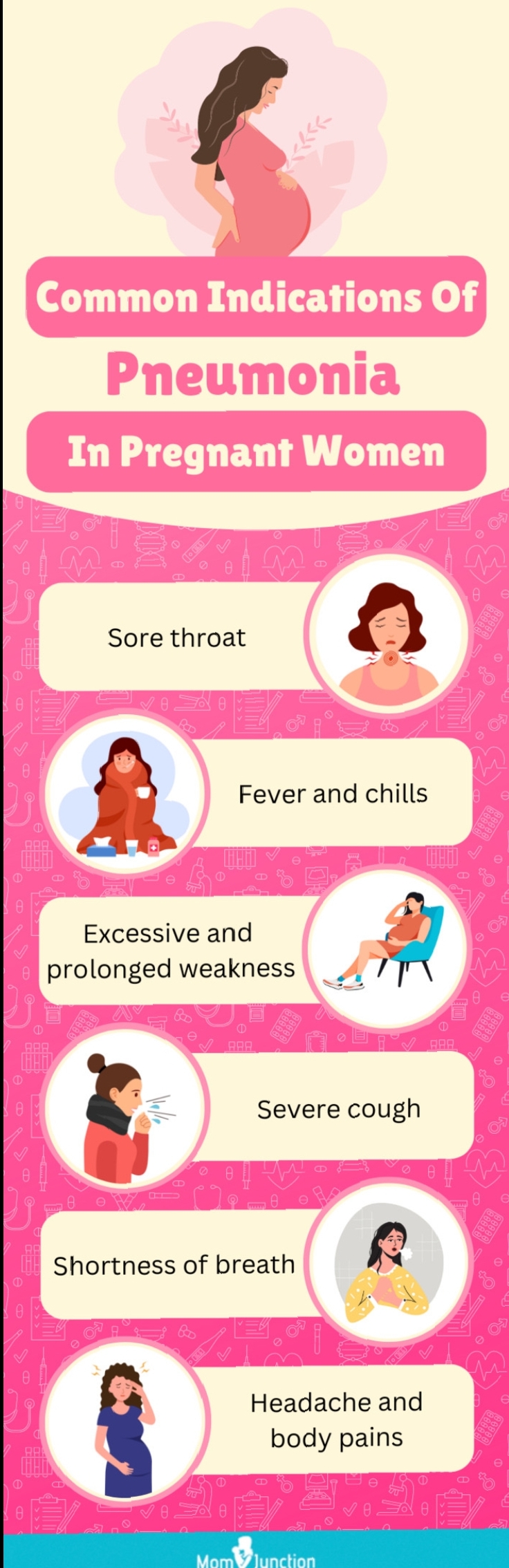
abstract: · pneumonia · during · pregnancy · has been associated with increased morbidity and mortal ...
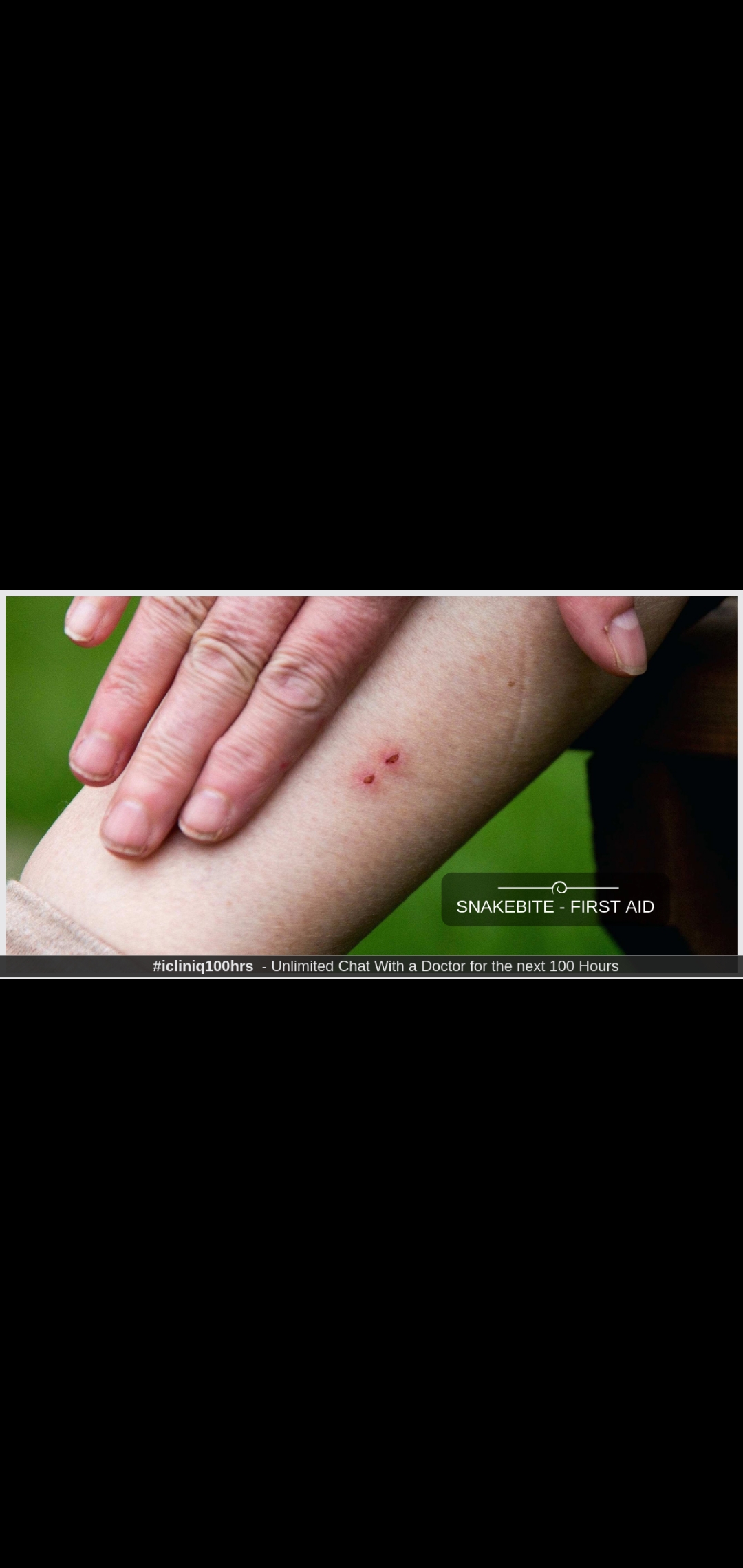
Abstract: · All Around the world, snake bite is the · envenomation it is Envenomation it is the nam ...
Related professionals
You may be interested in these jobs
-

Branch Sales Executive
1 day ago
Direct apply
HIRVA HR SOLUTIONS PRIVATE LIMITED Mumbai, IndiaA **Branch Sales Executive** is an expert who is reliable for the growth of their Career. They work with their sales group to create mutually profitable proposals, deal with contract terms, and communicate actually with stakeholders. · **Job Profile**: · - Deal with the walk-in c ...
-
Home Visit Phlebotomist_ Mumbai
23 hours ago
Indira IVF Navi Mumbai, IndiaJob Description · Roles & Responsibilities : · To identify the patient before performing a collection · To screen and collect sample from the patients · To collect the correct amount of sample for the ordered test · To label the collection correctly · To choose the appropriate c ...
-

Sales Man
1 day ago
Direct apply
Mahalakshmi Medicals Thoraipakkam, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, IndiaMedical shop sales man · 2year's experience · **Salary**: From ₹9,000.00 per month · Day range: · - Monday to Friday · - Weekend availability · Shift: · - Day shift · - Evening shift · Supplemental pay types: · - Yearly bonus · Ability to commute/relocate: · - Thoraipakkam, Chenn ...

Comments