PNEUMONIA
Author :- Mansuri Sohail (4004) ,MBBS Student .
Karganda Medical University PNEUMONIA :- Introduction , Pathogenesis , Diagnosis , Treatment & Prevention.
Introduction - Pneumonia is a respiratory infection that affects the lungs, causing inflammation in the air sacs. It can be caused by various infectious agents, leading to symptoms ranging from mild to severe. Pneumonia can affect people of all ages but poses a greater risk to young children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of pneumonia to increase awareness and promote effective management of this condition .Pneumonia is widespread and continues to cause a significant burden. The 2015 Global Infectious Disease Survey found that lower respiratory tract infections (LRIs) are the leading cause of infection and the fifth leading cause of death overall. Pneumococcal pneumonia is responsible for 55% (1.5 million deaths) of LRTI deaths in all age groups.
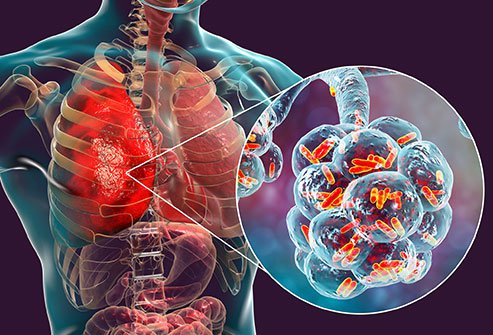
Pathogenesis - The pathogenesis of pneumonia involves a series of steps and interactions between the infectious agent, the respiratory tract, and the immune system. The process can vary depending on the specific causative agent, but here is a general overview of the pathogenesis of Pneumonia.
1)Entry and colonization: The infectious agent, such as bacteria or viruses, gains entry into the respiratory tract. This can occur through inhalation of droplets containing the pathogens or aspiration of bacteria from the upper respiratory tract or stomach. The infectious agent then colonizes the respiratory tract, primarily targeting the alveoli (small air sacs in the lungs).
2) Adherence and evasion: The pathogens adhere to the respiratory epithelial cells, allowing them to establish a foothold and avoid clearance mechanisms. Some bacteria possess specific adhesion molecules or pili that facilitate attachment to host cells. At the same time, pathogens employ various strategies to evade or subvert the immune response, such as production of enzymes that degrade immune proteins or toxins that damage host tissues.
3)Invasion and inflammation: The pathogens invade the respiratory epithelial cells, disrupting the normal functioning of the lung tissue. This triggers an immune response characterized by inflammation. The immune cells, including neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes, are recruited to the infected site, releasing cytokines and other inflammatory mediators. The inflammatory response aims to eliminate the infection but can also cause damage to lung tissues.
4) Alveolar consolidation and impairment of gas exchange: In bacterial pneumonia, the pathogens proliferate within the alveoli, causing consolidation (solidification) of the affected lung tissue. This consolidation leads to impaired gas exchange, resulting in symptoms such as difficulty breathing and decreased oxygen levels. In viral pneumonia, the viral replication within the respiratory epithelial cells can lead to cell death and disruption of the normal lung architecture.
5) Resolution or progression: The outcome of pneumonia depends on various factors, including the individual's immune response, the virulence of the infectious agent, and the availability and effectiveness of treatment. In some cases, the immune system successfully eliminates the infection, and the lung tissue gradually heals. However, if the immune response is overwhelmed or the causative agent is particularly virulent, pneumonia can progress and result in severe complications, including lung abscesses, pleural effusion, or sepsis.
Diagnosis - Diagnosis of Pneumonia: Diagnosing pneumonia involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Healthcare professionals will inquire about symptoms, conduct a thorough physical examination (including listening to lung sounds), and may order additional tests. Chest X-rays are commonly used to visualize the lungs and identify signs of infection or inflammation. Blood tests can help determine the presence of infection and the causative agent.In some cases, a sample of phlegm or lung fluid may be collected for laboratory analysis to identify the specific pathogen responsible.
Treatment - Treatment for pneumonia depends on the underlying cause, the severity of symptoms, and the overall health of the individual. Bacterial pneumonia is typically treated with antibiotics targeted at the specific bacteria causing the infection. Viral pneumonia, which does not respond to antibiotics, is managed with supportive care such as rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to alleviate symptoms. Severe cases of pneumonia or those associated with complications may require hospitalization for more intensive treatment, including intravenous antibiotics, oxygen therapy, and respiratory support.
Prevention - Preventing pneumonia involves various strategies aimed at reducing the risk of infection. Vaccination is a crucial preventive measure, particularly for certain populations at higher risk, such as young children, older adults, and individuals with underlying health conditions. Vaccines against Streptococcus pneumoniae, influenza viruses, and other pathogens are available and recommended. Practicing good hand hygiene, covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with sick individuals can help reduce the spread of respiratory infections.Additionally, maintaining overall health, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep, can support a strong immune system and reduce the susceptibility to pneumonia.
Conclusion - Pneumonia is a respiratory infection that can range from mild to severe, affecting individuals of all ages. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking prompt medical.
There is strong evidence that oral hygiene can reduce the risk of death from pneumonia, and it appears to be a preventative treatment for older adults without pneumonia. and has been shown to be effective in preventing pneumonia.
Reference -
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC website provides comprehensive information on pneumonia, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. You can visit their website at .
World Health Organization (WHO): The WHO offers valuable resources on pneumonia, including global statistics, treatment guidelines, and prevention strategies. Their website can be accessed at .
Mayo Clinic: The Mayo Clinic's website offers a wealth of information on various medical conditions, including pneumonia. They provide detailed articles on the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures for pneumonia. You can visit their website at
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): The NHLBI provides educational materials and resources related to lung health, including pneumonia. Their website offers information on pneumonia symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment options. You can find their resources at
American Lung Association (ALA): The ALA website provides information on lung diseases, including pneumonia. They offer articles and resources to help individuals understand pneumonia, its causes, treatment options, and preventive measures. Visit their website at
HealthArticles from Sohail Mansuri
View blog
MANSURI SOHAIL · Keywords – SUBSTANCES,HARMFUL USE,ETIOLOGY,TREATMENT. · Abstract- This is a modern ...
CERVICAL CANCER: RISK FACTORS, SCREENING, PREVENTION. · STUDENT OF KARAGANDA MEDICAL COLLEGE (KMU), ...
Diabetes mellitus · Diabetes mellitus · REVIEW ARTICLE · Overview: DIABETES MELLITUS · MANSURI SOHAI ...
Related professionals
You may be interested in these jobs
-
IBM MQ Administrator
5 days ago
Cateina Technologies Mumbai/Bangalore, India permanentJob Title : IBM MQ Administrator · Experience : 6 or more years · Overview : · We seek a skilled IBM MQ Administrator to join our team in ensuring our messaging infrastructure's smooth operation and optimization. The ideal candidate will have substantial experience in administeri ...
-
Technical Advisor
14 hours ago
KBR Gurugram, India Full timeTitle: · Technical Advisor - Mechanical (Rotating) OVERVIEW · KBR's history is built on the pioneers that set the standard across a variety of industries over the last century. Today, we continue that legacy by developing groundbreaking solutions for government and industry cl ...
-
Senior Principal AI/ML Engineer
4 days ago
GSK Bengaluru, India OTHERSite Name: Bengaluru Luxor North Tower · Posted Date: Apr · At GSK we are building a best-in-class data and prediction powered team that is ambitious for patients. We have already delivered unprecedented change over the past four years, improving R&D, becoming a leader in Consum ...



Comments